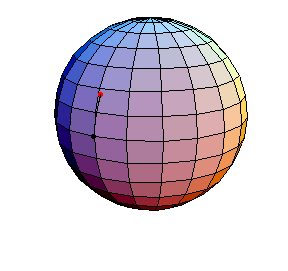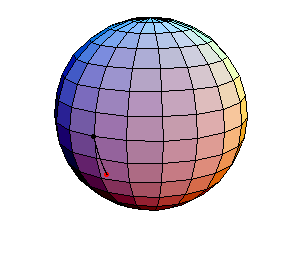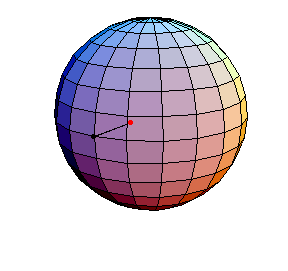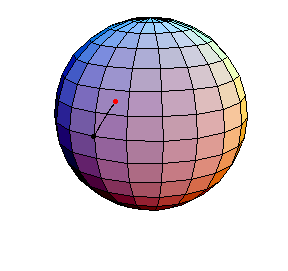
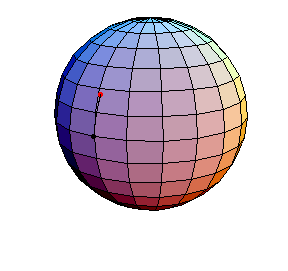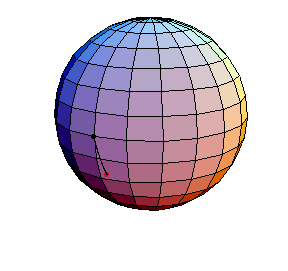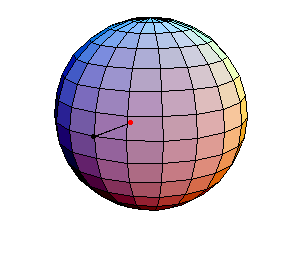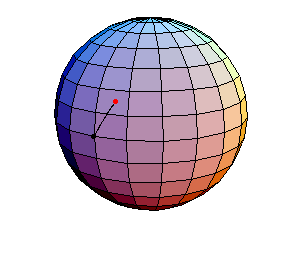
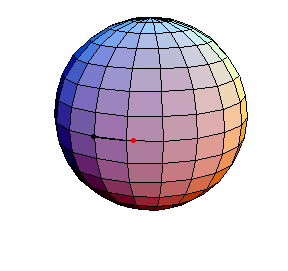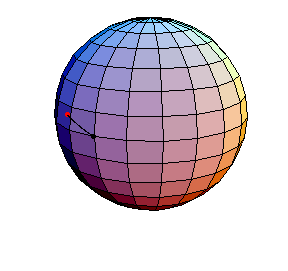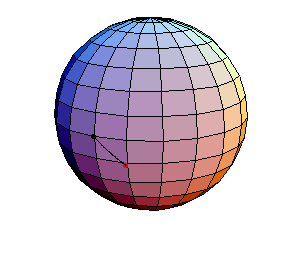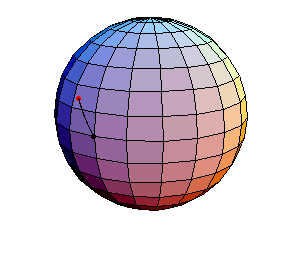
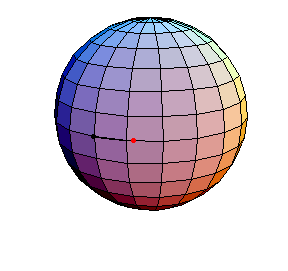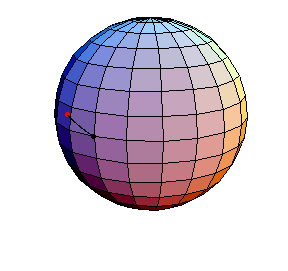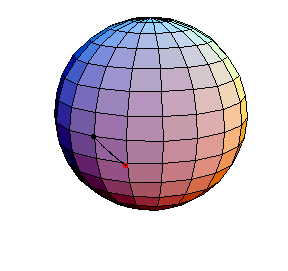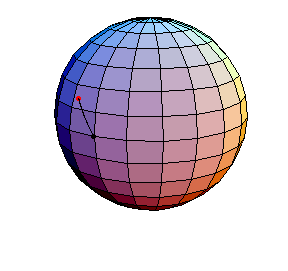
This is a small-amplitude oscillation about the stable equilibrium. The period is essentially 2πR.
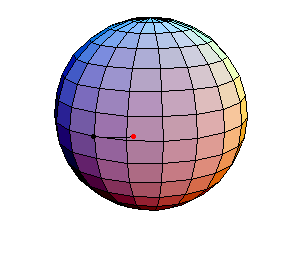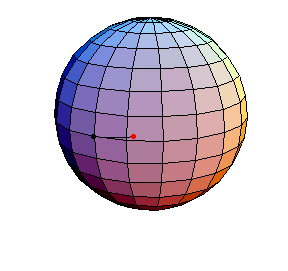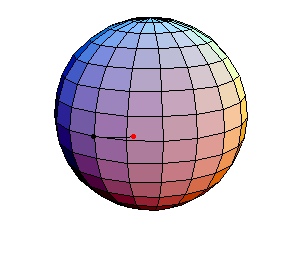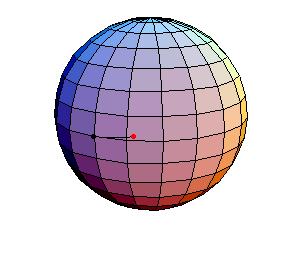
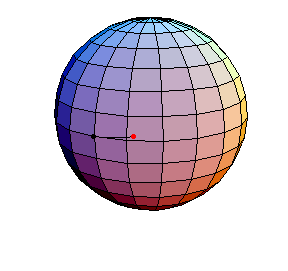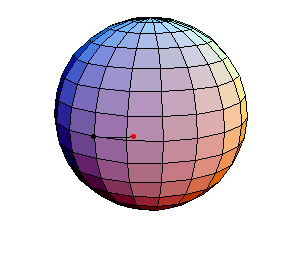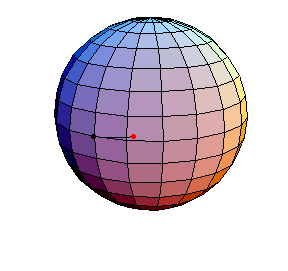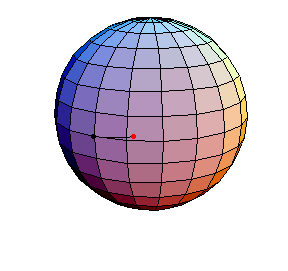
Pendulum Motion Due to Curvature
The Pendulum on S2
All of these have d/R = 2/5, where d is the length of the pendulum and R is the radius of the sphere.
θ(0) = .1, θ'(0) = 0
This is a small-amplitude oscillation about the stable equilibrium. The period
is essentially 2πR.


θ(0) = 1.5, θ'(0) = 0
This is a large oscillation about the stable equilibrium.
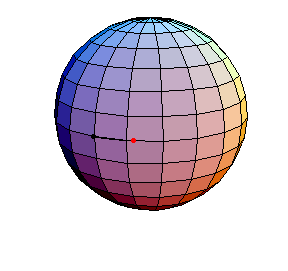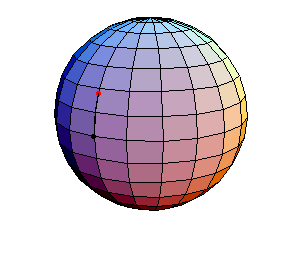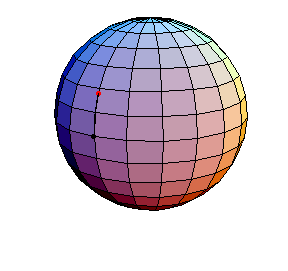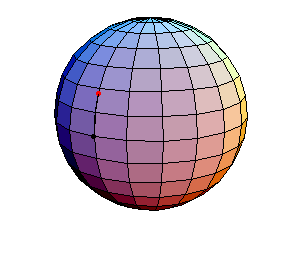
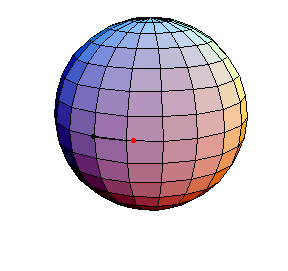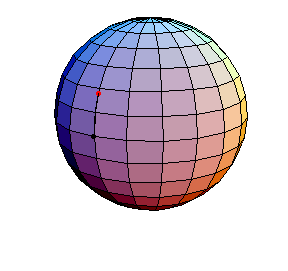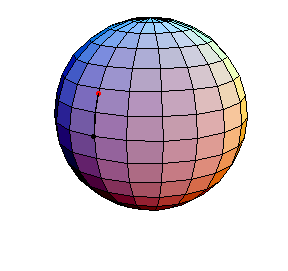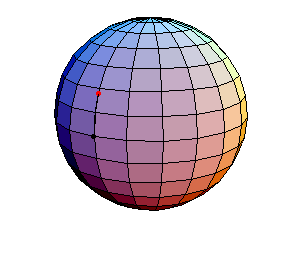
The next three start at the stable equilibrium with different values of
θ'(0) illustrating that θ'(0) = 1 separates oscillatory and orbital
behavior.
θ(0) = 0, θ'(0) = .99
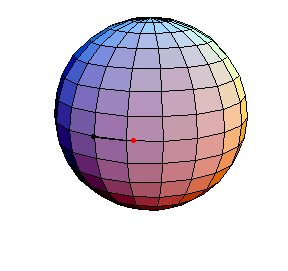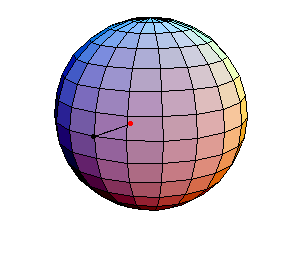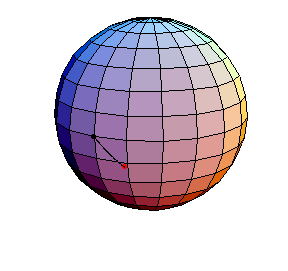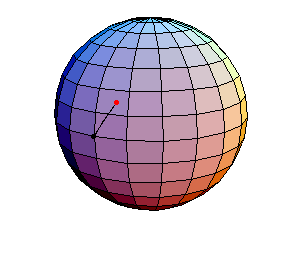
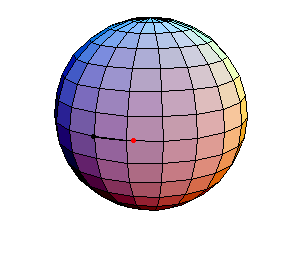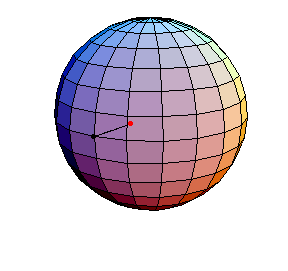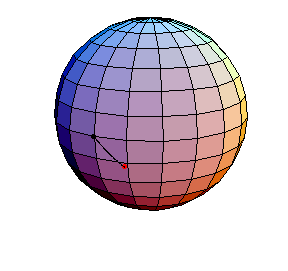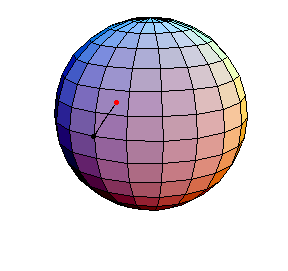
θ(0) = 0, θ'(0) = 1
θ(0) = 0, θ'(0) = 1.01
The Pendulum on H2
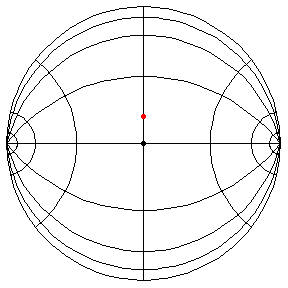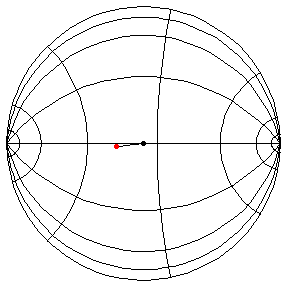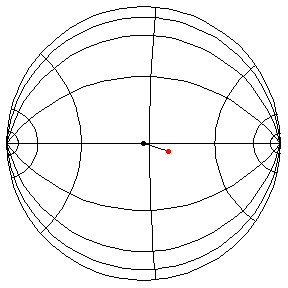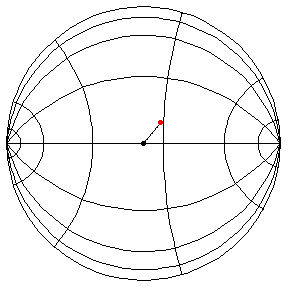
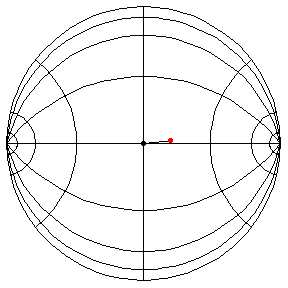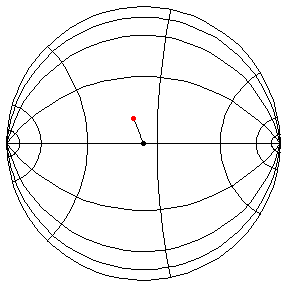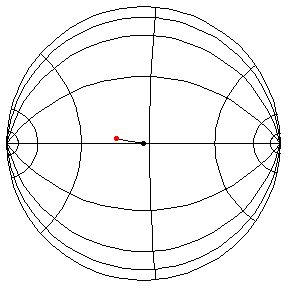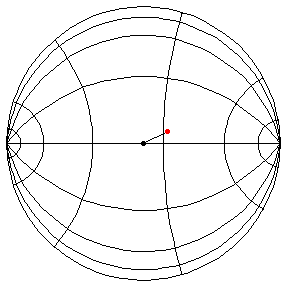
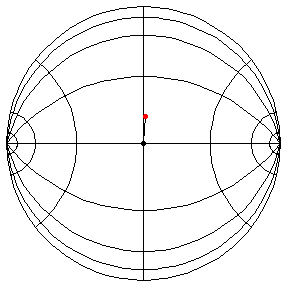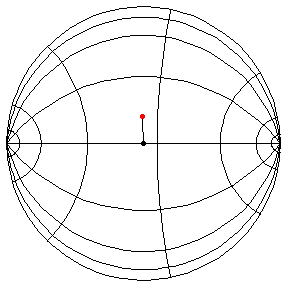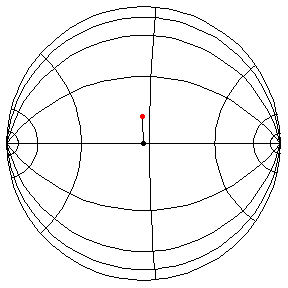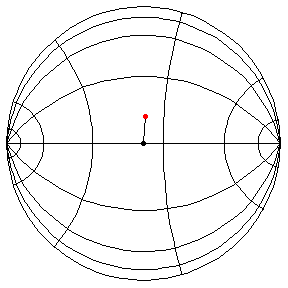
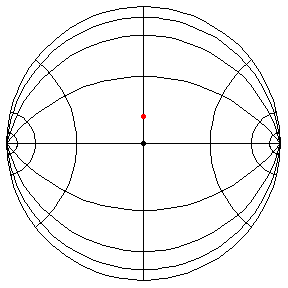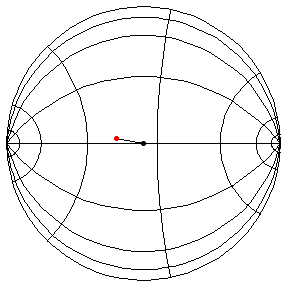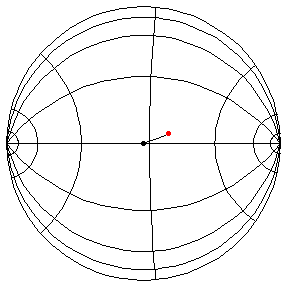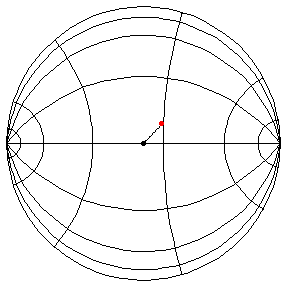
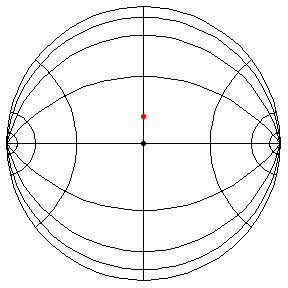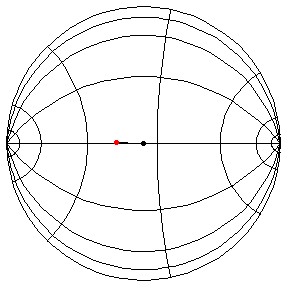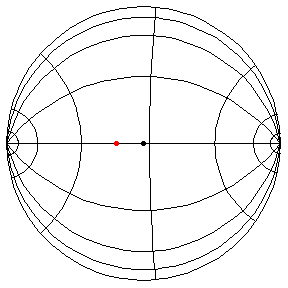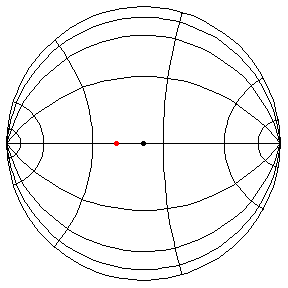
These are in the Poincare disk model. The horizontal line through the center is the geodesic along which the pivot travels. The other horizontal curves are equally-spaced equidistant curves. The vertical curves are equally spaced geodesics perpendicular to the path of the pivot. (This situation is identical to that on S2.) All of these have d/R = 2/5, where d is the length of the pendulum and R = √(-K), and K is the Gaussian curvature.
θ(0) = .1, θ'(0) = 0
This is a large oscillation about the stable equilibrium.
θ(0) = 1.5, θ'(0) = 0
This is a small-amplitude oscillation about the stable equilibrium. The period
is essentially 2πR.
The next three start at the stable equilibrium with different values of
θ'(0) illustrating that θ'(0) = 1 separates oscillatory and orbital
behavior.
θ(0) = π/2, θ'(0) = .99
θ(0) = π/2, θ'(0) = 1
θ(0) = π/2, θ'(0) = 1.01